Pipeline
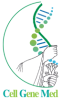
PIPELINE OVERVIEW
CLINICAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM FOR AUTOLOGOUS MSC-NTF CELLULAR THERAPY
ABOUT ALS
CLINICAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAM FOR AUTOLOGOUS MSC NTF CELLS IN ALS
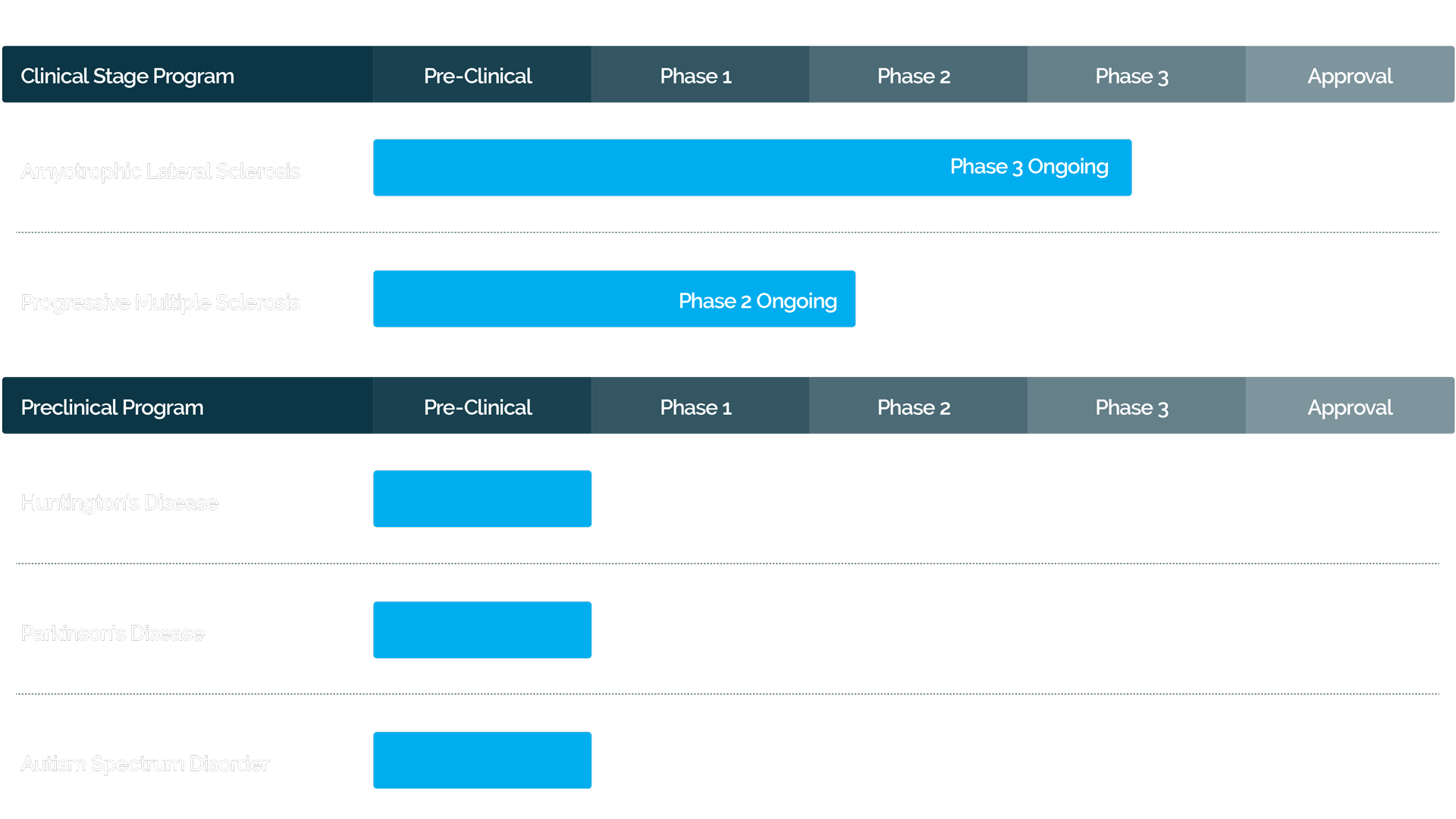
SUMMARY OF PHASE 2 TRIALS OF CELL-GENE COMPANY’S AUTOLOGOUS MSC-NTF CELLULAR THERAPY IN ALS
Administration of autologous MSC-NTF cells was found to be safe and well tolerated with the majority of adverse events being mild or moderate in severity Reduction in rate of ALS disease progression was observed in the autologous MSC-NTF treatment group but not in the placebo treatment group, and the treatment effect was statistically significant in a subpopulation of participants with more rapid disease progression. CSF biomarkers confirmed the secretion of NTFs and a reduction in inflammatory activity in the patients treated MSC-NTF-treated. Results from this study have been presented at major medical congresses. NEALS and AAN2018.
Study
N
Outcomes
Phase 2 (United States)
Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, single dose
NCT02017912
48
Administration of autologous MSC-NTF cells was found to be safe and well tolerated with the majority of adverse events being mild or moderate in severity Reduction in rate of ALS disease progression was observed in the autologous MSC-NTF treatment group but not in the placebo treatment group, and the treatment effect was statistically significant in a subpopulation of participants with more rapid disease progression. CSF biomarkers confirmed the secretion of NTFs and a reduction in inflammatory activity in the patients treated MSC-NTF-treated. Results from this study have been presented at major medical congresses. NEALS and AAN2018.
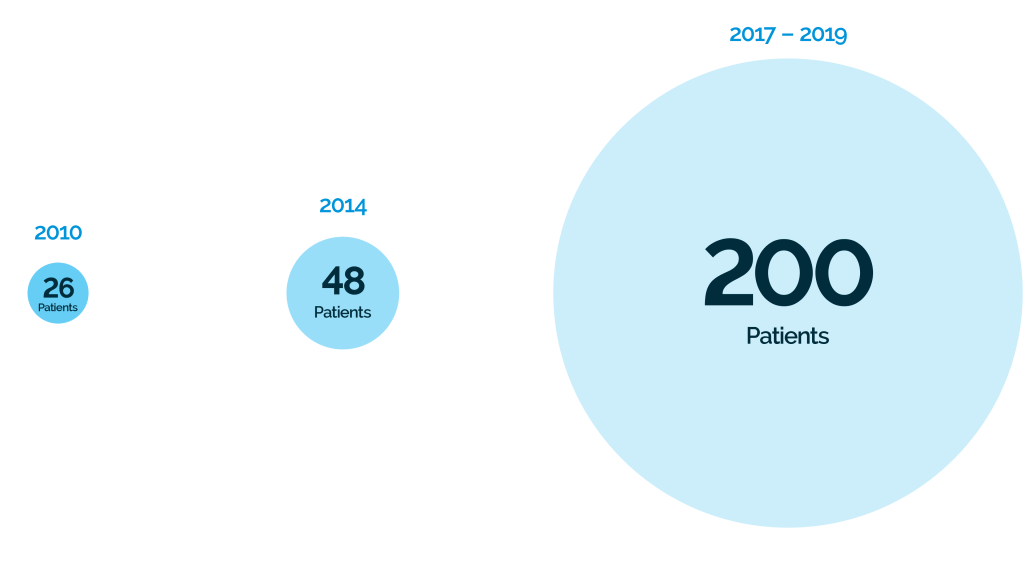
ABOUT ALS PHASE 3 PIVOTAL TRIAL (NCT03280056)
Warning: Illegal string offset 'pins_more_option' in /home/h288443/public_html/grantcell/wp-content/plugins/devvn-image-hotspot/admin/inc/add_shortcode_devvn_ihotspot.php on line 23
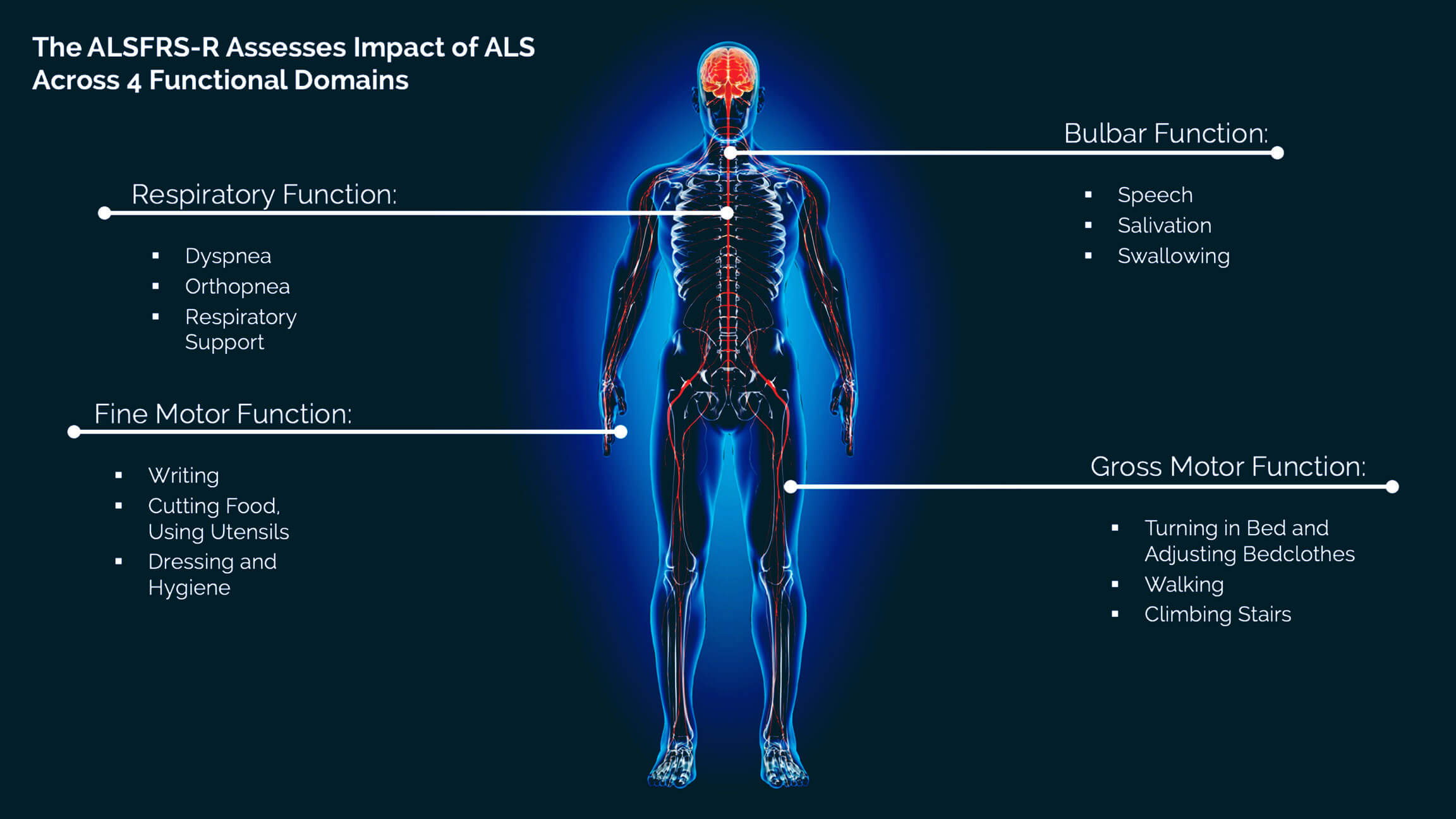
ABOUT THE ALSFRS-R
The rate of decline in ALSFRS-R scores is an important predictor of survival and disease prognosis.4 Without treatment, the average rate of decline on the ALSFRS-R is about 1 point per month.5
ABOUT PROGRESSIVE MS
CLINICAL DEVELOPMENT
PROGRAM IN PROGRESSIVE MS
RECENT CELL-GENE COMPANY PUBLICATIONS AND PRESENTATIONS
REFERENCES
1. Brown RH and Al-Chalabi A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:162-172.
2. Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, et al. The ALSFRS-R: a revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. J Neurol Sci. 1999;169(1-2):13-21
3. Leigh PN, Swash M, Iwasaki Y, et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a consensus viewpoint on designing and implementing a clinical trial. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2004;5:84-98.
4. Kaufmann P, Levy G, Thompson JL, et al. The ALSFRSr predicts survival time in an ALS clinic population. Neurology. 2005;64:38-43.
5. Castrillo-Viguera C, Grasso DL, Simpson E, et al. Clinical significance in the change of decline in ALSFRS-R. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2010;11:178-180.
6. Lublin FD, et al. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2014;83:278-286.
7. Confavreux C and Vukusic C. Natural history of multiple sclerosis: a unifying concept. Brain. 2006;129:606-616.
8. Chataway J. Tackling progression in multiple sclerosis. Editorial. The Lancet Neurology June 2018.
9. Harris, VK, et al. Characterization of autologous mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitors as a feasible source of stem cells for central nervous system applications in multiple sclerosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1:536-547.
10. Martins LF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells secretome-induced axonal outgrowth is mediated by BDNF. Scientific Reports. 2017;7:4153. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-03592-1; 11.
11. Rivera FR and Aigner L. Adult mesenchymal stem cell therapy for myelin repair in multiple sclerosis. Biol Res. 2012;45:257-268.